Vitamin E
A complex vitamin that protects the heart and eyes.

What is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E mainly functions in the body as an antioxidant, which helps prevent damage caused by free radicals—rogue forms of oxygen that wreak havoc with the fats found in the outer layer, or membrane, of all cells.
As nutrients go, vitamin E is more complex than most: there are actually eight forms of vitamin E found naturally in foods, each with a different level of biological activity in the body. However, alpha-tocopherol is the only form that is known to meet the body’s requirement for vitamin E, and it is the form on which the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is based.*

Why is Vitamin E Important?
Vitamin E supports heart health by preventing the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL, or “bad” cholesterol) by free radicals in the arteries. It also can prevent the oxidation of the fatty portion of the cell membranes in the lens of your eye. Vitamin E also plays a role in immune function.*
Recommended Dietary Allowance
Sources of Vitamin E
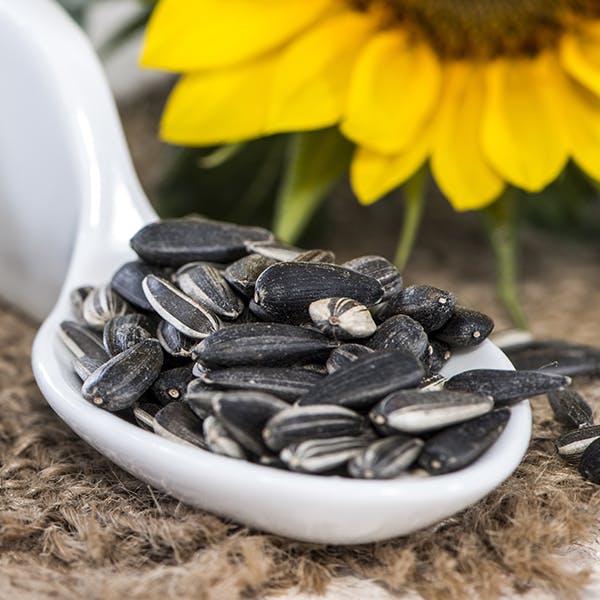

Sunflower Seeds
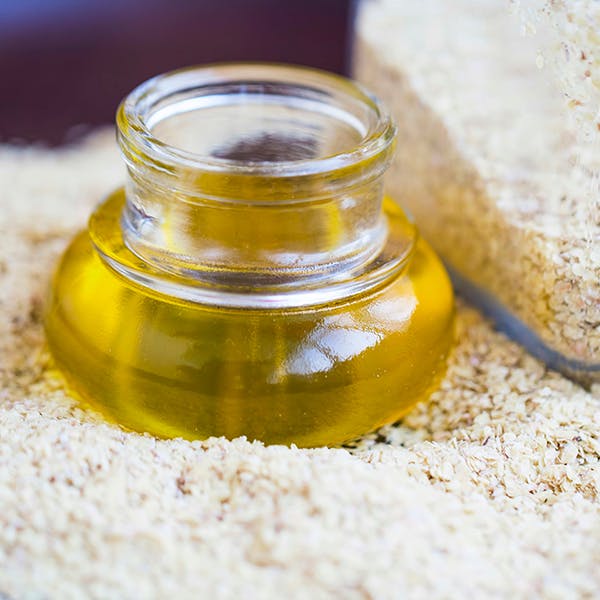

Wheat Germ Oil

Almonds
Centrum Silver

A daily multivitamin formulated for adults 50+ to help promote heart health, brain function, and eye health.
Centrum MultiGummies
Multi + Antioxidants
A tasty multivitamin packed with antioxidants to support immune and brain function, vitality, stress response, and cellular health.*
Vitamin E Helps Support
Recommended Articles
Explore Additional Vitamins & Minerals
* This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.