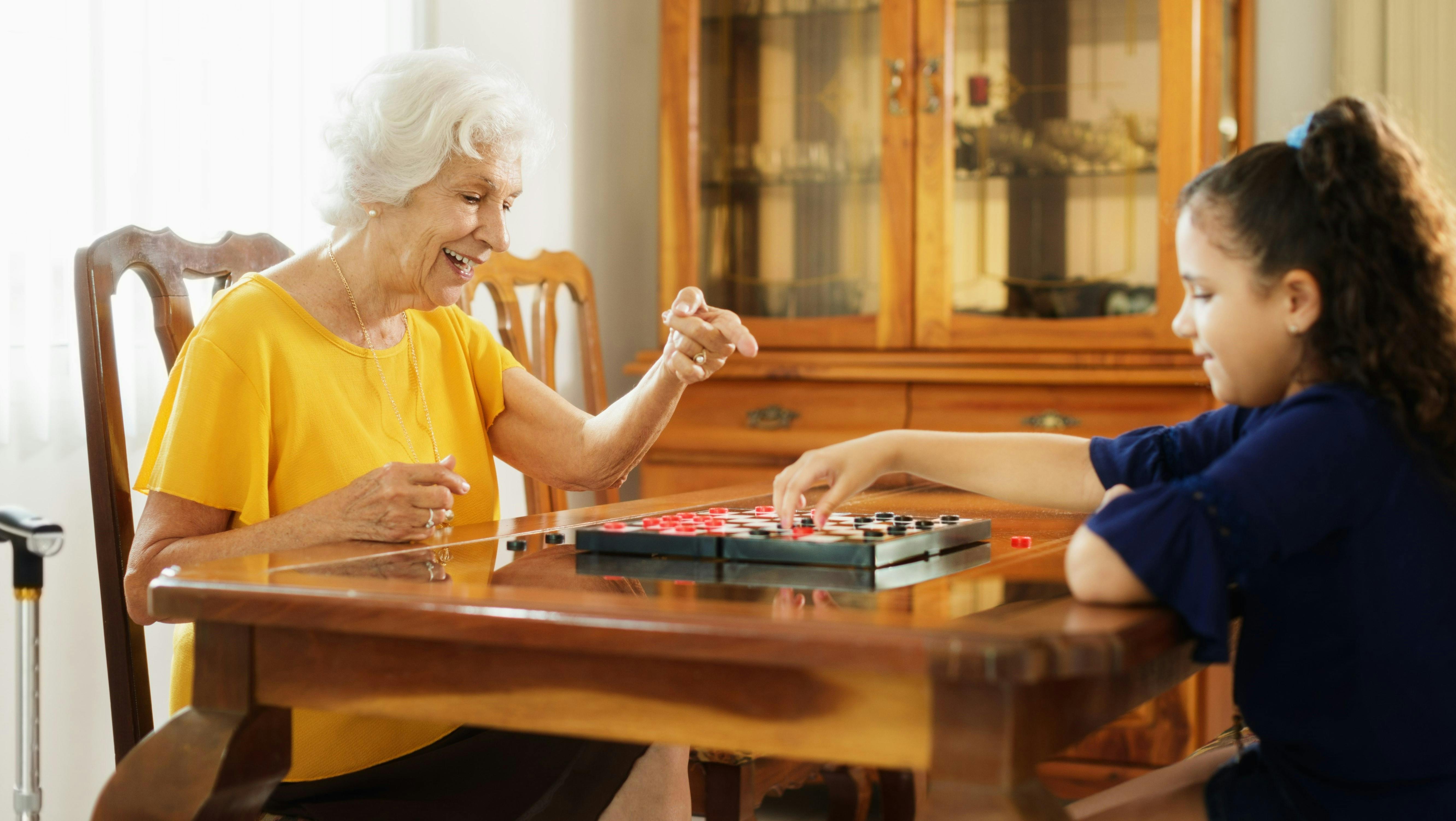
Folic Acid
(Vitamin B9)
The synthetic form of folate, a B vitamin, that’s necessary for cell reproduction and cellular health during pregnancy and periods of rapid growth.

What Is Folic Acid?
Folic acid is the synthetic counterpart to folate, a B vitamin that can be found naturally in certain plant foods. Of the two, folic acid is the more readily available—the body absorbs about twice as much folic acid at any given time—but they play the same role in good health.
Cell reproduction is among folate’s most important duties. Folic acid plays an important role in the production of red blood cells. In conjunction with vitamins B6 and B12, it helps control homocysteine levels in the bloodstream. Research indicates that elevated homocysteine levels could potentially be associated with heart disease.[1]
Folate is also necessary for making the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, which is a critical role during times of rapid growth, such as pregnancy and infancy.[2] This also explains why folate/folic acid is so important in maintaining normal brain function.[2]
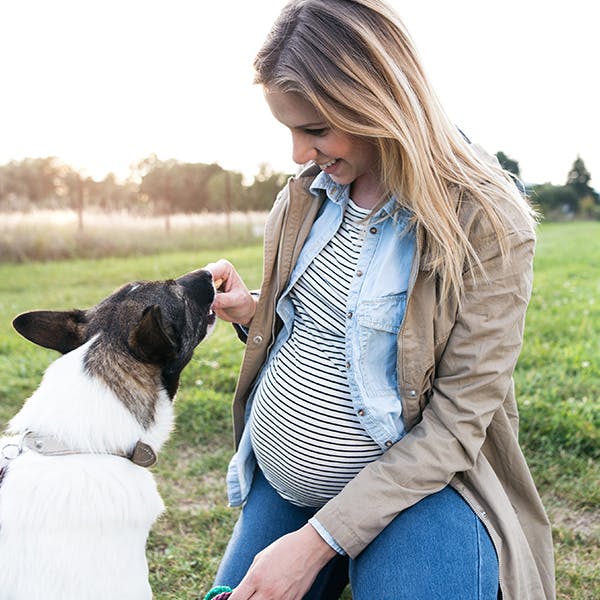

Why Is Folic Acid Important?
Adequate folic acid is necessary during pregnancy to help prevent certain birth defects and support neural tube development. The USDA’s 2015 Dietary Guidelines for Americans identifies folic acid as a nutrient needed for women in their childbearing years. Taking a prenatal supplement starting three months before conception can help women meet their daily folic acid needs.[1]
Recommended Dietary Allowance (DFE*)
Centrum Silver

Specially formulated for women 50+ to help support heart health, brain function, healthy eyes, and strong bones.
Centrum Silver

A daily multivitamin formulated for adults 50+ to help promote heart health, brain function, and eye health.
Centrum Maternal Health

NEW! A daily multivitamin gummy that supports women before and during pregnancy. With folic acid, DHA, and 10 other essential nutrients, these gummies are a tasty way to support your body during pregnancy, as well as your baby’s development.*
Centrum Maternal Health

NEW! A gummy supplement formulated with Vitamin B6 to help moms-to-be find relief from occasional nausea and morning sickness.* These tasty gummies are made with real ginger.
Centrum Maternal Health

NEW! A multivitamin gummy that supports new moms with essential nutrients like Biotin for hair, skin, and nail health, Vitamin C for immune support, and Iodine to support baby's development through breastfeeding.*
Folic Acid Helps Support
Latest Articles
Explore Additional Vitamins & Minerals
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Source Citations:
- Folate (folic acid). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-folate/art-20364625. Accessed 11/5/23. Return to reference
- Folate. Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/?swcfpc=1. Accessed 01/26/2024. Return to reference